QIAseq FX Single Cell DNA Library Kit
Single-cell whole genome libraries with comprehensive coverage and high sequence fidelity
Single-cell whole genome libraries with comprehensive coverage and high sequence fidelity
The kit delivers exceptional genome coverage from single cells, including regions with high GC-content. In comparison to PCR-based methods of whole genome amplification, the multiple displacement annealing technology included in the QIAseq FX Single Cell DNA Library Kit eliminates PCR duplicates and minimizes GC-bias, ensuring high library diversity and maximizing genome coverage, even from single cells. Additionally, the high-fidelity MDA reaction introduces fewer sequencing errors, reducing false positives and thus enables more sensitive mutation detection. The low background and comprehensive coverage makes this kit an excellent option for the analysis of aneuploidy, copy number variations and mutations from single cells.
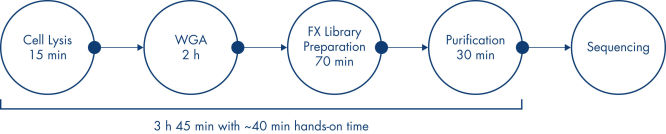
This kit relies on three key technologies to deliver high-diversity whole genome libraries from single cells. After cell lysis, a high-fidelity MDA reaction is used to amplify µg-amounts of gDNA using the high-fidelity phi29 polymerase. The amplified gDNA is then fragmented into short inserts using a highly random enzymatic DNA fragmentation reaction. The FX fragmentation does not require the entire sample of input gDNA, and the excess can be stored for later use or confirmatory testing. The fragmented gDNA is then packaged into an NGS-compatible library with a novel, single-tube library preparation. The entire process, beginning with an isolated single cell, is PCR-free and requires around 3.5 hours to complete.
The QIAseq FX Single Cell DNA Library Kit is a complete cell-to-library solution that includes all of the reagents necessary to generate high-diversity whole genome libraries from single eukaryotic or bacterial cells or from limited amounts of intact gDNA. The kit contains reagents for the effective cell lysis of isolated single cells or small clusters of cells, for example from laser-capture microdissection platforms. After lysis, genomic DNA is amplified using an ultra-high fidelity multiple displacement annealing technology. Using viable cells as input, this procedure generates large amounts of amplified gDNA. This amplified gDNA is subjected to a random and efficient enzymatic fragmentation method, which cleaves the DNA into shorter fragments compatible with any Illumina NGS instrument. These fragments are then end-polished and subjected to a highly efficient ligation reaction with the included, single-use adapters. This effectively captures the fragmented DNA into a library, which can be purified using standard methods prior to sequencing. Additional PCR amplification of the library is unnecessary, and the entire procedure is PCR-free, eliminating the possibility of introducing PCR duplicates and maximizing library diversity.