✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
RNeasy Protect Mini Kit (50)
Cat. No. / ID: 74124
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- Immediate in RNA stabilization and protection
- Reliable gene expression and gene-profiling data
- No need for liquid nitrogen, dry ice, or phenol
- Ready-to-use, high-quality total RNA in minutes
- No CsCl gradients, no LiCl or ethanol precipitation
Product Details
RNeasy Protect Mini Kits enable stabilization of RNA in tissue samples, RNA and DNA in sorted or cultured cells, RNA in human saliva samples and RNA in bacterial samples. The RNeasy Protect Mini Kit and Bacteria Mini Kit include RNeasy spin columns for purifying up to 100 µg of high-quality RNA using silica-membrane technology. The RNeasy Protect Cell Mini Kit provides the RNeasy Plus Mini Kit for purification of total RNA. The RNeasy Protect Saliva Mini Kit includes the RNeasy Micro Kit, which purifies and concentrates total RNA using specialized RNeasy MinElute spin columns.
The RNeasy Protect Mini, RNeasy Protect Cell Mini and RNeasy Protect Bacteria Mini Kits can be automated on the QIAcube Connect.
Performance
The RNA-stabilizing properties of RNAprotect Tissue Reagent prevent gene induction or down-regulation triggered by sample manipulation allowing you to preserve and analyze the gene expression profile. The RNeasy and RNAprotect bundle enables isolation of high-quality RNA (see figure " Prevention of degradation of mRNA in tissues"). In addition, RNeasy purified RNA from RNAprotect stabilized samples remains intact following storage of tissue samples under a wide variety of conditions (see figure " Stable RNA in tissues"). A range of tissue types can be processed with the RNeasy Protect Mini Kit (see table “Total RNA yields obtained with RNeasy Protect Mini Kit”).
Total RNA yields obtained with RNeasy Protect Mini Kit
| Mouse tissue | Amount (mg) | Average yield* (µg) |
|---|---|---|
| Brain | 10 | 10 |
| Liver | 10 | 43 |
| Lung | 10 | 12 |
| Spleen | 10 | 45 |
The RNeasy Protect Cell Mini Kit is ideal for gene expression analysis experiments where cells need to be delivered from one lab to another (see table “Higher RNA yields from leukocytes* preserved for 10 days in RNAprotect Cell Reagent”).
Higher RNA yields from leukocytes* preserved for 10 days in RNAprotect Cell Reagent
| Assay result | RNAprotect Cell Reagent | RNAprotect Tissue Reagent |
|---|---|---|
| RNA yield using RNeasy technology (µg) | 10 | 3.5 |
| Real-time RT-PCR of abl (CT value) | 25 | 26 |
Cells in RNAprotect Cell Reagent can be stored or transported for up to 1 day at 30ºC, up to 7 days at room temperature (15–25ºC), or up to 4 weeks at 2–8ºC, and can also be stored long-term at –20ºC or –80ºC (see table “Intact RNA from Jurkat cells stored at ambient temperature”, and figures " Effective inhibition of PMA induction" and " More reliable quantification of CD83 transcript") allowing you to preserve and analyze the gene expression profile.
Intact RNA from Jurkat cells stored at ambient temperature
| Cell storage conditions | RIN value of purified RNA* |
|---|---|
| 30ºC (1 day) | 9.8 |
| 25ºC (7 days) | 9.7 |
| 2–8ºC (28 days) | 10 |
| –20ºC (28 days) | 9.8 |
| –80ºC (28 days) | 9.8 |
Saliva stabilized with RNAprotect Saliva Reagent can be stored or transported for up to 1 day at 37°C, up to 14 days at room temperature (15–25°C), or up to 4 weeks at 2–8°C, or can be archived at –20°C or –80°C (see figure " Effective stabilization of β-actin transcript") allowing you to preserve and analyze the gene expression profile. Purified RNA from saliva, as an alternative to blood, allows microarray analysis for research into oral and systemic diseases, and gene expression analysis of RNA biomarkers for cancer by real-time RT-PCR (see figures " Minimization of transcript degradation in saliva" and " Stable mRNA levels of cancer biomarkers").
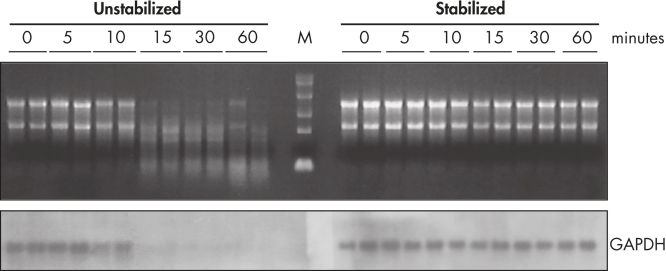
During traditional methods for cell harvesting and RNA isolation, enzymatic degradation of RNA leads to reduction or loss of many transcripts. The reduction is particularly significant in bacterial mRNA molecules, which have very short half lives of only a few minutes. In addition, genes can be induced during handling and processing of bacterial samples, leading to higher expression. Use of RNAprotect Bacteria Reagent overcomes these problems by providing immediate stabilization prior to RNA isolation (see figures " RNAprotect Bacteria Reagent prevents mRNA degradation" and " Accurate gene expression profiles") allowing you to preserve and analyze the gene expression profile. Yield from E. coli (6 x 108 cells) is 100 µg of RNA and the RNA yield from Bacillus subtilis (1 x 108 cells) is 15 µg. RNA purified with the kit is high-quality with A260/A280 ratios of 1.9–2.1 (measured in 10 mM Tris·Cl, pH 7.5).
RNA purified with RNeasy technology has A260/A280 ratios of 1.9–2.1 (measured in 10 mM Tris·Cl, pH 7.5). Since the RNeasy procedure enriches for RNA species >200 nt, RNA yield does not include 5S rRNA, tRNAs, or other low-molecular-weight RNAs.
See figures
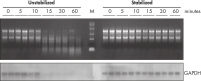 Stable RNA in tissues: different temperatures and freeze–thaw cycles.
Stable RNA in tissues: different temperatures and freeze–thaw cycles. Effective inhibition of PMA induction.
Effective inhibition of PMA induction.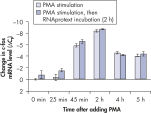 More reliable quantification of CD83 transcript.
More reliable quantification of CD83 transcript.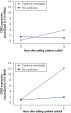 Effective stabilization of beta-actin transcript.
Effective stabilization of beta-actin transcript.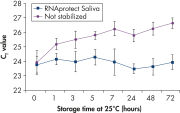 Minimization of transcript degradation in saliva.
Minimization of transcript degradation in saliva. Stable mRNA levels of cancer biomarkers.
Stable mRNA levels of cancer biomarkers.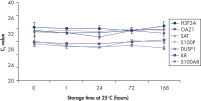 RNAprotect Bacteria Reagent prevents mRNA degradation.
RNAprotect Bacteria Reagent prevents mRNA degradation.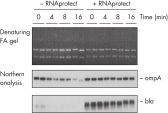 Accurate gene expression profiles.
Accurate gene expression profiles.
Principle
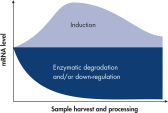
The RNeasy Protect system – consisting of an RNeasy and RNAprotect bundle – provides a complete RNA protection and isolation solution, from sample harvesting to pure RNA, in one kit. Proven RNeasy silica-membrane technology in spin-column format, combined with the RNA-stabilizing properties of RNAprotect Reagents, allows purification of high-quality, intact RNA. Once a biological sample is harvested, its RNA becomes extremely unstable (see figure " Changes in mRNA levels"). Innovative RNAprotect Reagents immediately stabilize and protect the RNA expression pattern. Samples can be archived without risk of RNA degradation, even after multiple freeze–thaw cycles. Following stabilization, RNeasy technology simplifies total RNA isolation by combining the stringency of guanidine-isothiocyanate lysis with the speed and purity of silica-membrane purification (see figure " RNeasy Mini spin column").
See figures
Procedure
Samples can be stabilized and stored in RNAprotect Tissue Reagent, included in RNeasy Protect Kits. For RNA purification, samples (0.5–30 mg tissue) are first lysed and then homogenized. Ethanol is added to the lysate to provide ideal binding conditions. The lysate is then loaded onto the RNeasy silica membrane (binding capacity up to 100 µg RNA). RNA binds, and all contaminants are efficiently washed away. Pure, concentrated RNA is eluted in 30–100 µl water (see flowchart "RNeasy Protect Mini procedure"). RNA purification can be automated on the QIAcube Connect.
Sorted or cultured cells are mixed with RNAprotect Cell Reagent, which immediately stabilizes the cellular RNA. After RNA stabilization, total RNA is purified using the RNeasy Plus Mini Kit (see flowchart " RNeasy Protect Cell procedure"). The cells in RNAprotect Cell Reagent are centrifuged, and the resulting cell pellet is lysed and homogenized in Buffer RLT Plus. The lysate is then passed through a gDNA Eliminator spin column, which rapidly and effectively removes genomic DNA. Ethanol is added to the lysate, which is then applied to an RNeasy spin column. After centrifugation, total RNA binds to the membrane of the RNeasy spin column. Contaminants are efficiently washed away, and high-quality total RNA is eluted in 30–50 µl of RNase-free water. Purification of DNA, or of RNA and DNA, requires the additional purchase of a QIAGEN DNA purification kit. Details are provided in the RNAprotect Cell Reagent Handbook.
Saliva (200 µl) collected from a donor is immediately mixed with RNAprotect Saliva Reagent to stabilize the RNA in the saliva. Total RNA is purified from stabilized saliva using the RNeasy Micro Kit (see flowchart " RNeasy Protect Saliva procedure"). The saliva sample is first centrifuged, and Buffer RLT is then added to the resulting pellet. After addition of ethanol, the sample is applied to an RNeasy MinElute spin column, where RNA binds to the membrane after centrifugation. Traces of genomic DNA are removed by DNase digestion, and contaminants are washed away in several wash steps. Highly pure RNA is then eluted using RNase-free water in a volume of just 14 µl. RNAprotect Saliva Reagent also stabilizes DNA. Protocols for purification of DNA, or RNA and DNA, from stabilized saliva are available.
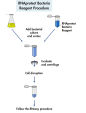
Two volumes of RNAprotect Bacteria Reagent are added directly to 1 volume of bacterial culture (≤7.5 x 108 bacteria) prior to RNA isolation, providing immediate stabilization of RNA (see flowchart " RNAprotect Bacteria Reagent procedure"). The stabilization allows time for efficient bacterial lysis using a choice of protocols: enzymatic lysis, mechanical disruption, or a combination of both methods. We recommend the TissueLyser II for efficient mechanical disruption. Ethanol is then added to the lysate to provide ideal binding conditions. The lysate is loaded onto the RNeasy silica membrane (binding capacity 100 µg RNA). Following RNA binding, all contaminants are efficiently washed away. Pure, concentrated RNA is eluted in 30–100 µl of water. The RNeasy Protect Bacteria Mini Kit can be automated on the QIAcube Connect.
Amounts of RNA isolated from bacteria can vary due to species and growth conditions. The RNeasy Protect Bacteria Mini Kit is suitable for use with a wide range of bacterial species, both Gram positive (e.g.,Staphylococcus aureus and Mycobacterium avium) and Gram negative (e.g.,Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium). Bacteria grown in either minimal or complex medium can be used. Since the RNeasy procedure enriches for RNA species >200 nucleotides, RNA yield does not include 5S rRNA, tRNAs, or other low-molecular-weight RNAs. RNeasy Protect Bacteria Kits provide the highest-quality RNA with minimum copurification of DNA. For certain RNA applications that are sensitive to very small amounts of DNA, the residual amounts of DNA remaining can be removed using the RNase-Free DNase Set for convenient on-column DNase treatment during the RNeasy procedure.
See figures
Applications
RNA purified with RNeasy technology is ideal for use in all applications. Downstream applications include:
- RNA-seq
- Quantitative, real-time RT-PCR
- End-point RT-PCR
- Northern, dot, and slot blotting
- Array analysis
- Poly A+ RNA selection
| Features | RNeasy Protect Mini Kit | RNeasy Protect Cell Mini Kit | RNeasy Protect Saliva Mini Kit | RNeasy Protect Bacteria Mini Kit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Applications | RNA-seq, PCR, qPCR, real-time RT-PCR, microarray | RNA-seq, PCR, qPCR, real-time RT-PCR, microarray | RNA-seq, PCR, qPCR, real-time RT-PCR, microarray | RNA-seq, PCR, qPCR, real-time RT-PCR, microarray |
| Elution volume | 30–100 µl | 30–50 µl | 8–14 µl | 30–100 µl |
| Format | Spin column | Spin column | Spin column | Spin column |
| Main sample type | Tissue samples | Cultured cells | Saliva samples | Bacteria |
| Processing | Manual (centrifugation) | Manual (centrifugation) | Manual (centrifugation) | Manual (centrifugation) |
|
Purification of total RNA, miRNA, poly A+ mRNA, DNA or protein |
RNA | RNA | RNA | RNA |
| Sample amount | 0.5–30 mg | Max. 107 cells | 200 µl | 15–100 µg |
| Stabilization | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Technology | Silica technology | Silica technology | Silica technology | Silica technology |
| Time per run or per prep | – | – | – | 20 minutes |
| Yield | 10–45 µg | Varies | Varies | 8–70 µg |
Supporting data and figures
Prevention of degradation of mRNA in tissues.