Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads
Für die Hochdurchsatz-Aufreinigung von Proteinen mit His-tag im Mikro-Maßstab und vielseitige Magnetocapture-Assays mit His-tags
Für die Hochdurchsatz-Aufreinigung von Proteinen mit His-tag im Mikro-Maßstab und vielseitige Magnetocapture-Assays mit His-tags
Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads sind mit Ni-NTA-Agarose-Affinitätsaufreinigungsmatrix beschichtete Magnetpartikel. Sie dienen der Immobilisierung und Aufreinigung rekombinanter Proteine mit His-tag. Histidin-Reste im His-tag binden mit hoher Spezifität und Affinität an die freien Positionen der Koordinationssphäre der immobilisierten Nickelionen. Sobald die Proteine gebunden sind, können die Beads mit einem Magneten präzipitiert, gewaschen und die Proteine in kleinen Puffervolumina unter nativen oder denaturierenden Bedingungen eluiert werden.
Das QIAexpress Ni-NTA Protein Purification System, einschließlich der Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads (siehe Abbildung Mikrofotografie der magnetischen Ni-NTA-Agarose-Beads), basiert auf der herausragenden Selektivität des patentierten Ni-NTA(Nickel-Nitrilotriessigsäure)-Harzes für Proteine mit einem Affinitätstag aus sechs oder mehr Histidinresten – dem His-tag. Diese Technologie erlaubt die Ein-Schritt-Aufreinigung nahezu jedes Proteins mit His-tag aus beliebigen Expressionssystemen unter nativen oder denaturierenden Bedingungen (siehe Abbildung Proteinaufreinigung mit dem Ni-NTA-Proteinaufreinigungssystem). NTA, das über vier Chelationen-Bindestellen für Nickelionen verfügt, bindet Nickel fester als metallchelatbildende Aufreinigungssysteme, die nur drei verfügbare Bindestellen für die Interaktion mit Metallionen besitzen. Die zusätzliche Chelation-Bindestelle verhindert das Auswaschen von Nickelionen und führt zu einer höheren Bindungskapazität und damit zu Proteinpräparationen mit höherer Reinheit verglichen mit denen, die mit anderen metallchelatbildenden Aufreinigungssystemen gewonnen wurden. Das QIAexpress System kann für die Aufreinigung von Proteinen mit His-tag aus jedem Expressionssystem, einschließlich Baculoviren, Säugerzellen, Hefen und Bakterien verwendet werden.
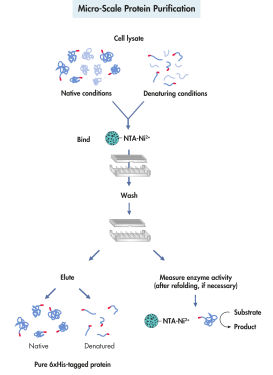
Die Aufreinigung von Proteinen mit His-tag besteht aus 4 Phasen: Zelllyse, Bindung, Waschen und Elution (siehe Abbildung Proteinaufreinigung im Mikro-Maßstab). Die Aufreinigung rekombinanter Proteine mit dem QIAexpress System ist nicht von der dreidimensionalen Struktur des Proteins oder des His-tags abhängig. Dadurch ist eine Ein-Schritt-Proteinaufreinigung sowohl unter nativen als auch unter denaturierenden Bedingungen, ausgehend von verdünnten Lösungen und Rohlysaten, möglich. Starke denaturierende Agenzien und Detergenzien können für eine effiziente Solubilisierung und Aufreinigung von Rezeptoren, Membranproteinen und Proteinen, die Einschlusskörper (Inclusion bodies) bilden, eingesetzt werden. Reagenzien, die eine effiziente Entfernung unspezifisch bindender Kontaminanten ermöglichen, können den Waschpuffern hinzugefügt werden (siehe Tabelle). Die aufgereinigten Proteine werden unter milden Bedingungen durch Zugabe von 100–250 mM Imidazol als Kompetitor oder durch Absenkung des pH-Werts eluiert.
| Denaturierende Agenzien | Detergenzien | Reduzierende Agenzien | Sonstige | Salze | Für die langfristige Lagerung |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 M Gu-HCl | 2 % Triton X-100 | 20 mM β-ME | 50 % Glycerin | 4 M MgCl2 | Bis zu 30 % Ethanol |
| 8 M Harnstoff | 2 % Tween 20 | 10 mM DTT | 20 % Ethanol | 5 mM CaCl2 | oder 100 mM NaOH |
| 1 % CHAPS | 20 mM TCEP | 20 mM Imidazol | 2 M NaCl |
Das QIAexpress Ni-NTA Protein Purification System einschließlich der magnetischen Ni-NTA Agarose-Beads ermöglicht eine zuverlässige Ein-Schritt-Aufreinigung von Proteinen, die sich für verschiedenste Applikationen eignen, einschließlich:
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Applications | Proteomik |
| Processing | Automatisiert/manuell |
| Yield | < 10 mg Protein je Säule |
| Bead size | 20–70 µm |
| Support/matrix | Magnetische Agarose-Beads |
| Tag | 6xHis-tag |
| Special feature | Hoher Durchsatz (96-well) |
| Start material | Zelllysat |
| Binding capacity | Bis zu 2-mg/ml-Suspension (5 %) |
| Scale | Mikro-Maßstab |