QIAGEN Large-Construct Kit
Zur Aufreinigung von bis zu 50 μg BAC-, PAC- und P1-DNA oder bis zu 200 μg Cosmid-DNA, frei von genomischer DNA
Zur Aufreinigung von bis zu 50 μg BAC-, PAC- und P1-DNA oder bis zu 200 μg Cosmid-DNA, frei von genomischer DNA
✓ Automatische Verarbeitung von Online-Bestellungen 24/7
✓ Sachkundiger und professioneller technischer und Produkt-Support
✓ Schnelle und zuverlässige (Nach-)Bestellung
Kat.-Nr. / ID. 12462
✓ Automatische Verarbeitung von Online-Bestellungen 24/7
✓ Sachkundiger und professioneller technischer und Produkt-Support
✓ Schnelle und zuverlässige (Nach-)Bestellung
Das QIAGEN Large-Construct Kit umfasst Anionenaustauschsäulen nach dem Schwerkraftprinzip für die Aufreinigung von großmolekularer DNA. Ein neuartiger integrierter ATP-abhängiger Exonuklease-Verdauungsschritt sichert die selektive Entfernung von genomischer DNA-Kontamination. Die aufgereinigte DNA entspricht der durch zweimalige CsCl-Gradientenzentrifugation gewonnenen DNA und eignet sich zur Transfektion.
Bei der DNA-Aufreinigung mit dem QIAGEN Large-Construct Kit kommt ein optimiertes Verfahren nach dem Schwerkraftprinzip zum Einsatz, das eine deutlich höhere Reinheit der DNA als andere gängige Methoden liefert. Eine neuartige integrierte Behandlung mit ATP-abhängiger Exonuklease ermöglicht die effiziente Entfernung genomischer DNA.
Das innovative Anionenaustauscherharz in den QIAGEN-Spitzen, die Teil des QIAGEN Large-Construct Kits sind, wurde ausschließlich für die Aufreinigung von Nukleinsäuren entwickelt. Seine hervorragenden Trenneigenschaften führen zu einer DNA-Reinheit, die der durch zwei aufeinanderfolgende Durchgänge der CsCl-Gradientenzentrifugation erzielten Reinheit gleichwertig oder überlegen ist. Die vorverpackten QIAGEN-Spitzen (siehe Abbildung „ Anionenaustauscher-Spitzen“) arbeiten nach dem Schwerkraftprinzip und trocknen nie aus, was den Zeitaufwand für die manuelle Plasmidpräparation minimiert. Im gesamten QIAGEN Plasmid-Aufreinigungssystem kommen keine toxischen Substanzen wie Phenol, Chloroform, Ethidiumbromid und CsCl zum Einsatz, was die Gefahr für den Anwender und die Umwelt minimiert.
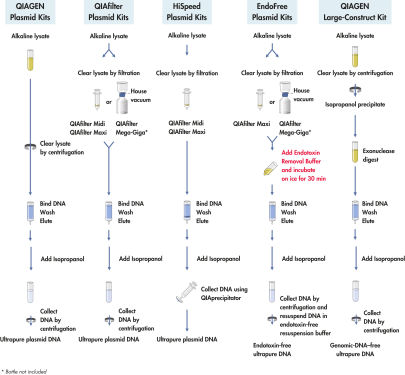
Nach der alkalischen Lyse von bis zu 500 ml Kulturmedium (siehe Flussdiagramm „ QIAGEN Plasmid-Kit-Verfahren“) sorgt ein spezieller integrierter Verdauungsschritt mit ATP-abhängiger Exonuklease für die selektive Entfernung kontaminierender genomischer DNA sowie DNA-Konstrukte mit Nicks oder Schäden. Die Probe wird dann auf die Anionenaustauscher-Spitze aufgebracht, wo die Plasmid-DNA unter entsprechenden salzarmen und pH-Bedingungen selektiv gebunden wird. RNA, Proteine, Metaboliten und andere niedermolekulare Verunreinigungen werden durch eine Waschlösung mit mittlerem Salzgehalt entfernt. Die genomische DNA-freie, reine Plasmid-DNA wird in einem stark salzhaltigen Puffer eluiert. Die DNA wird konzentriert, durch Isopropanol-Fällung entsalzt und durch Zentrifugation gesammelt.
Die mit dem QIAGEN Large-Construct Kit aufgereinigte DNA eignet sich für jede Anwendung, einschließlich:
| Eigenschaften | Spezifikationen |
|---|---|
| Plasmid type | BAC, PAC, P1, cosmid DNA |
| Applications | Subklonierung, Transfektion, Sequenzierung usw. |
| Processing | Manuell (Zentrifugation) |
| Culture volume/starting material | <500 ml Kulturvolumen |
| Samples per run (throughput) | 1 Probe pro Lauf |
| Technology | Anionenaustausch-Technologie |
| Time per run or prep per run | 280 min |
| Yield | <150 ug |