RT2 Profiler PCR Arrays
For pathway-focused gene expression analysis using laboratory-verified assays
For pathway-focused gene expression analysis using laboratory-verified assays
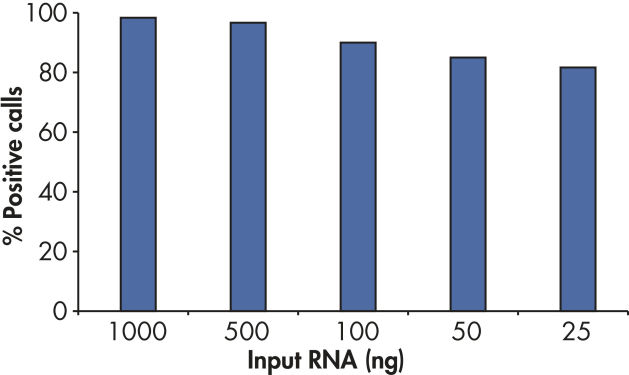
With the sensitivity of the RT2 First Strand Kit, as little as 1 ng or as much as 5 µg of total RNA per array plate provides greater than 80% present call rates (see figure " Positive results with as little as 25 ng RNA").
The complete PCR array system demonstrates strong correlations across technical replicates, lots, and instruments with average correlation coefficients >0.99, ensuring reliable detection of differences in expression between biological samples (see figure " High reproducibility among different users").
The PCR array system, with high-quality input RNA, yields single bands of the predicted size without primer-dimers or other secondary products, therefore providing the highly accurate real-time PCR results (see figure " A single gene-specific product in every reaction").
Uniform PCR amplification efficiency is required for the PCR array technology to allow accurate comparisons of gene expression across all genes and all samples. The unique combination of our proprietary primer design algorithm and rigorous testing of every primer assay guarantees the high performance of every primer assay on PCR arrays (see figure " PCR arrays yield highly accurate results").
RT² Profiler PCR Arrays are tested and optimized in combination with the RT² SYBR Green qPCR Mastermixes and the RT² First Strand Kit. This testing means that RT² Profiler PCR Array performance is guaranteed when all three of these components are used together.
RT2 Profiler PCR Arrays are reliable tools for analyzing the expression of a focused panel of genes. Each 96-well plate, 384-well plate or 100-well disc PCR array includes SYBR® Green-optimized primer assays for a thoroughly researched panel of relevant, pathway- or disease-focused genes. RT2 Profiler PCR Arrays can also be customized to contain a panel of genes tailored to your specific research interests. The high-quality primer design and RT2 SYBR® Green qPCR Mastermix formulation enable the PCR array to amplify 96 or 384 different gene-specific products simultaneously under uniform cycling conditions.
This combination provides the RT2 Profiler PCR Array with the specificity and the high amplification efficiencies required for accurate real-time SYBR® Green results. PCR arrays are easy to use in any research laboratory.
RT2 Profiler PCR Arrays are sensitive enough for use with RNA prepared from regular samples (0.1–5 µg RNA), FFPE samples, and small samples (1–100 ng RNA). >
Simply mix the cDNA template with the appropriate ready-to-use PCR mastermix, aliquot equal volumes to each well of the same plate, and then run the real-time PCR cycling program (see flowchart " Simple procedure"). RT2 Profiler PCR Arrays are compatible with all QIAGEN, ABI, Bio-Rad, Eppendorf, Roche, and Stratagene instruments.
RT2 Profiler PCR Arrays are available in 96-well plate, 384-well plate, and 100-well disc formats, and are used to monitor the expression of 84 or 370 genes related to a disease state or pathway, plus 5 housekeeping genes. Each RT2 Profiler PCR Array also includes control elements for:
Data can be analyzed using an easy-to-use Excel-based data analysis template or Web-based software. Data analysis is based on the ΔΔCT method with normalization of the raw data to either housekeeping genes.
RT² PCR Profiler Arrays can be used in all areas of biological and medical research, including: