Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads
Hisタグ付きタンパク質のハイスループット、微小規模精製、およびHisタグを使用する多用途磁気捕捉アッセイ用
Hisタグ付きタンパク質のハイスループット、微小規模精製、およびHisタグを使用する多用途磁気捕捉アッセイ用
Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beadsは、Ni-NTA Agaroseアフィニティー精製マトリックスでコーティングされた磁性粒子です。Hisタグを持つ組み換えタンパク質の固定化と精製に使用します。Hisタグのヒスチジン残基は、固定化したニッケルイオンの配位圏の空いた位置に、高い特異性と親和性で結合します。タンパク質が結合すると、磁石を使ってビーズを沈殿させ、洗浄し、天然または変性条件下で少量のバッファーにタンパク質を溶出させることができます。
Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads(図 Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beadsの顕微鏡写真を参照)を含むQIAexpress Ni-NTAタンパク質精製システムは、6個以上のヒスチジン残基のアフィニティタグ(Hisタグ)を含むタンパク質に対する特許取得済みのNi-NTA(ニッケル-ニトリロ三酢酸)樹脂の優れた選択性に基づいています。この技術により、天然または変性条件下で、あらゆる発現系からほぼすべてのHisタグ付きタンパク質をワンステップ精製できます(図 Ni-NTAタンパク質精製システムによるタンパク質の精製を参照)。ニッケルイオンに対して4つのキレート部位を持つNTAは、金属イオンとの相互作用に利用できる部位が3つしかない金属キレート精製システムよりもしっかりとニッケルに結合します。余剰のキレート部位がニッケルイオンの浸出を防ぐため、他の金属キレート精製システムを使用した場合よりも結合能が高く、より高純度のタンパク質調製物が得られます。QIAexpressシステムを使用すると、バキュロウイルス、哺乳類細胞、酵母、細菌など、あらゆる発現系からHisタグ付きタンパク質を精製できます。
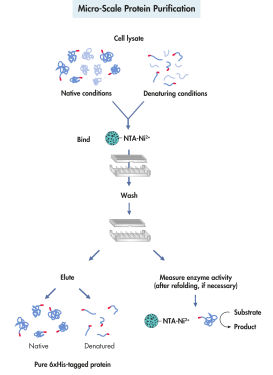
Hisタグ付きタンパク質の精製は、細胞溶解、結合、洗浄、溶出の4段階で構成されています(図 微小規模タンパク質精製を参照)。QIAexpressシステムを用いる組み換えタンパク質の精製は、タンパク質やHisタグの3次元構造に依存しません。これにより、希釈溶液や粗溶解物から、天然または変性条件下で、タンパク質をワンステップ精製できます。受容体、膜タンパク質、封入体を形成するタンパク質の効率的な可溶化と精製には、強力な変性剤や洗浄剤を使用できます。非特異的に結合する汚染物質を効率的に除去できる試薬を洗浄バッファーに含めることができます(表を参照)。精製したタンパク質は、競合剤として100~250 mMのイミダゾールを加えるか、pHを下げることにより、穏やかな条件下で溶出します。
| 変性剤 | 界面活性剤 | 還元剤 | その他 | 塩 | 長期保存用 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 M Gu·HCl | 2% Triton X-100 | 20 mM β-ME | 50%グリセロール | 4 M MgCl2 | 最大30%エタノール |
| 8 M尿素 | 2% Tween 20 | 10 mM DTT | 20%エタノール | 5 mM CaCl2 | または100 mM NaOH |
| 1% CHAPS | 20 mM TCEP | 20 mMイミダゾール | 2 M NaCl |
Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beadsを含むQIAexpress Ni-NTAタンパク質精製システムは、以下を含むあらゆるアプリケーションに適したタンパク質を高い信頼性でワンステップ精製します。
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Applications | プロテオミクス |
| Processing | 自動/手動 |
| Yield | カラムあたり<10 mgタンパク質 |
| Bead size | 20~70 µm |
| Support/matrix | 磁性アガロースビーズ |
| Tag | 6xHisタグ |
| Special feature | ハイスループット(96ウェル) |
| Start material | 細胞溶解物 |
| Binding capacity | 最大2 mg/ml懸濁液(5%) |
| Scale | 微小規模 |