QIAseq Tumor Mutational Burden Panels
For creating a comprehensive profile of Tumor Mutational Burden (TMB) and Microsatellite Instability Status (MSI)
For creating a comprehensive profile of Tumor Mutational Burden (TMB) and Microsatellite Instability Status (MSI)
Researchers face the challenge of creating a reliable, consistent workflow for easily processing samples to understand the mutational landscape of tumors. Tumor Mutational Burden (TMB) is the measure of the number of mutations found within a tumor. However, a lack of standardized testing has prevented any meaningful movement to create a TMB biomarker. The new QIAseq Tumor Mutational Burden Panels overcome the challenges of earlier assay designs to create a comprehensive profile of TMB and Microsatellite Instability (MSI) status by achieving high analytical sensitivity, with lower false and negative rates, while still maintaining >95% correlation with whole exome datasets. QIAseq NGS assays, including the QIAseq TMB and MSI Panels, have a fail rate of less than 5% for samples that have passed QC and provide a TMB score. The QIAseq TMB Panel has been tested in several key opinion leader labs and has performed as well or better than many earlier products. This comprehensive panel covers 486 genes and can be boosted to add 27 MSI markers. Want to try this solution for the first time? Request a quote for a trial.
Specifically, the QIAseq TMB Panel:
Need a quote for your research project or would you like to discuss your project with our specialist team? https://go.qiagen.com/ExiqoncomProductandServiceInformation
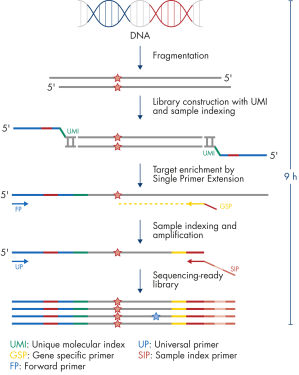
Each panel is a one-box, NGS platform-agnostic solution that contains all the necessary components, such as beads and key primers, to construct libraries from enriched genomic targets. Primer design is based on single primer extension, in which each genomic target is enriched by one target-specific primer and one universal primer – a strategy that removes conventional two target-specific primer design restriction and reduces the amount of required primers. All primers required for a panel are pooled into an individual primer pool to reduce panel handling and the number of pools required for enrichment and library construction. Platform-specific indexes, which are contained in a separate box, allow the multiplexing of up to 384 samples per sequencing run.
Performance table QIAseq TMB Panels and MSI:
PCR duplicates are a major issue in targeted DNA sequencing, since, through PCR amplification, they turn unique DNA molecules into identical DNA molecules that cannot be distinguished from each other. In addition, errors from PCR amplification and sequencing process may also be present in final reads that lead to false positive variants in sequencing results. This, in turn, results in the inability to confidently call DNA variants present at low frequencies in the starting DNA material. To overcome the issue of PCR duplicates and amplification artifacts, the QIAseq TMB Panels use digital sequencing by incorporating UMIs into the starting DNA material before any amplification takes place, thereby preserving the uniqueness of the starting DNA molecules and overcoming the issues of PCR duplicates, false positives and library bias.
The entire workflow of the QIAseq TMB Panels to go from extracted DNA to sequencing-ready libraries can be completed in 9 hours (see Figure "Workflow"). Extracted DNA is fragmented, genomic targets are molecularly bar coded and enriched, and libraries are constructed. Sequencing files can be fed into the QIAseq pipeline, a cloud-based data analysis pipeline, which will filter, map and align reads, as well as count unique molecular bar codes associated with targeted genomic regions, and call variants with a bar code-aware algorithm. This data can then be fed into IVA or QCI for interpretation.
The QIAseq TMB Panels can be used to call a variety of DNA variants from a wide range of sample types for numerous applications.
DNA variants:
Sample types:
Applications:
Content: