EndoFree Plasmid Kits
10 mgまでのエンドトキシンフリーなトランスフェクショングレードのプラスミドおよびコスミドDNA精製用
10 mgまでのエンドトキシンフリーなトランスフェクショングレードのプラスミドおよびコスミドDNA精製用
✓ オンライン注文による24時間年中無休の自動処理システム
✓ 知識豊富で専門的な製品&テクニカルサポート
✓ 迅速で信頼性の高い(再)注文
Cat. No. / ID: 12362
✓ オンライン注文による24時間年中無休の自動処理システム
✓ 知識豊富で専門的な製品&テクニカルサポート
✓ 迅速で信頼性の高い(再)注文
EndoFree Plasmid Kitsは陰イオン交換をベースにしたエンドトキシンフリーのプラスミドDNA精製を迅速に行ないます。QIAfilter Cartridgesはろ過による迅速なライセート清澄化を実現します。精製したDNA は、CsCl 密度勾配遠心法を2 回行なって得られる精製グレードに匹敵し、高感度トランスフェクション等のアプリケーションに最適です。EndoFree Plasmid Buffer Setは、10 megaまたは5 gigaのトランスフェクショングレードのプラスミドまたはコスミドDNA調製に使用できます。
EndoFree Plasmid Kitsには、リポ多糖類を除去するために追加の抽出ステップやアフィニティーカラムは不要で、プラスミド精製操作工程に効率的なエンドトキシン除去ステップが組み込まれています。QIAfilter Mega-GigaまたはMaxi Cartridgeによるろ過操作でバクテリアライセートを清澄化し、陰イオン交換樹脂の含有されたオープンカラム方式のQIAGEN-tips でプラスミドDNA を精製します。最大10 mg(Giga)、2.5 mg(Mega)、500 µg(Maxi)のDNAが培養液から精製されます(培養液量はプラスミドのコピー数、添加サイズ、宿主株、培養媒体に依存します)。精製したDNAは、エンドトキシンフリーです(0.1 EU/µg 以下のDNA)。
低コピー数のプラスミド、コスミドの精製では、必要な培養液量が多く、QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridgeの容量は制限があるため、EndoFree Plasmid Giga KitよりEndoFree Plasmid Mega Kitの使用をお薦めします。
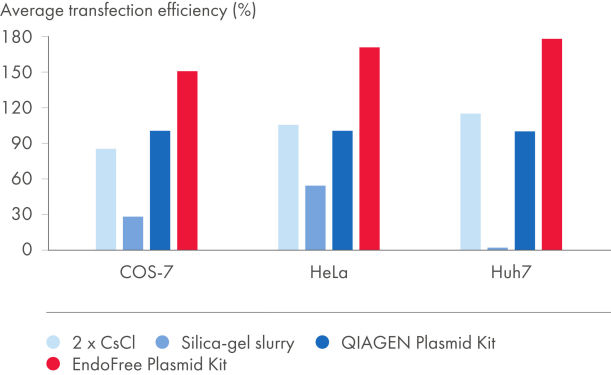
EndoFree Plasmid Kitsは、溶解ステップ中に放出され、初代細胞や感受性の高い細胞株へのトランスフェクションに影響を与えるバクテリアのエンドトキシンを除去します。EndoFree Plasmid Buffer Setを用いて得られたエンドトキシンを含まないDNAは、トランスクフェション実験に最適で、再現性が高く信頼できる結果が得られます(図“ プラスミド精製法とトランスフェクション効率の比較”および“ プラスミド純度とトランスフェクション効率の比較”、表 "異なるプラスミド調製法によるエンドトキシンレべルの比較”および“EndoFree DNAで初代培養細胞へ高いトランスフェクション効率)。QIAGENの超高純度なエンドトキシン・フリーなDNAは遺伝子治療研究やその他の高感度なアプリケーションに最適です。
| プラスミド調製法 | エンドトキシン (EU†/µg DNA) | トランスフェクション 効率の平均‡ |
|---|---|---|
| EndoFree Plasmid Kit | 0.1 | 154% |
| QIAGEN プラスミド調製用キット | 9.3 | 100% |
| 2x CsCl | 2.6 | 99% |
| シリカゲル懸濁液 | 1230.0 | 24% |
| DNA 精製法 | トランスフェクトされた細胞の割合 |
|---|---|
| EndoFree Plasmid Kit | 21.0% ± 0.93 |
| QIAGEN プラスミド調製用キット | 8.1% ± 0.57 |
| シリカゲル懸濁液 | 5.2% ± 0.74 |
精製したプラスミドDNA中のエンドトキシンの混入レベルは用いた精製法に依存します(表 “異なるプラスミド調製法によるエンドトキシンレべルの比較”)。シリカ懸濁液で精製したDNAは、非常に高いエンドトキシンレベルを示します。QIAGEN Plasmid Kits、QIAfilter およびHiSpeed Plasmid Kits そして2回のCsCl 密度勾配遠心分離法で調製した高純度のDNAは、比較的低いレベルのエンドトキシンしか含んでいません。エンドトキシン除去ステップが組み込まれたEndoFree Plasmid Buffer Setでは、プラスミドDNA 1 μg当たり0.1 EU以下のエンドトキシン含有量のプラスミドDNAが得られます。
QIAfilter Cartridges(EndoFree Plasmid Buffer Setには付属していない)は、バクテリア細胞のアルカリ溶解後に行なう遠心操作に代わる方法として開発された特別なフィルターです。QIAfilter CartridgesはSDS沈殿物を完全に取り除くばかりではなく、遠心操作に必要な時間よりも短時間でバクテリアライセートの清澄化を可能にし、プラスミド精製時間を最大1時間短縮できます。QIAfilter Cartridges(EndoFree Plasmid Buffer Setには付属していない)はバクテリアライセートを簡単かつ効率的に清澄化します。QIAfilter Maxi Cartridgesは、シリンジフォーマットで、液体を注入することにより溶解物がフィルターを通過し、すばやく清澄化されます。
QIAGEN-tip(EndoFree Plasmid Buffer Setには付属していない )中の非常にユニークな陰イオン交換樹脂は核酸精製を目的として開発されました。本製品の優れた核酸分離特性により、CsCl 密度勾配遠心分離法を2回行なって得たDNAの純度に匹敵、あるいはそれ以上の純度のDNAが調製されます。充填済みQIAGEN-tipsはオープンカラムで操作し、乾燥することはなく、プラスミド調製に必要なマニュアルでの作業時間を短縮できます。全てのQIAGENプラスミド精製システムでは、ユーザーおよび環境への危害が最小限となるように、フェノール、クロロホルム、臭化エチジウム、CsCl等の有害な試薬を一切使用していません。
リポ多糖類あるいはLPSとして知られているエンドトキシンはE. coli のようなグラム陰性菌の細胞膜構成成分です(図 “ バクテリア細胞壁”)。エンドトキシンはプラスミド精製の溶解ステップ中に放出され、エンドトキシン感受性細胞株へのトランスフェクション効率を顕著に低下させます(図“ プラスミド精製法とトランスフェクション効率の比較”および“ プラスミド純度とトランスフェクション効率の比較”)。さらにエンドトキシンはDNAと結合していない“フリー”のトランスフェクション試薬と競合することにより、トランスフェクション実験におけるプラスミドDNAの取り込みに影響を与えます。エンドトキシンの混在はまた、マクロファージやB 細胞のような免疫系細胞における免疫応答を非特異的に活性化するため、間違ったトランスフェクション解釈につながることもあります。これらの応答には、IL-1 やプロスタグランジン等のタンパク質や脂質の生産誘導も含まれています。全エンドトキシンの混入はトランスフェクション実験のセットアップにおいてコントロールできない変動要素となるため、実験結果およびその再現性に影響し、結果の比較および解釈が困難になります。さらに、エンドトキシンショック症候群や、補体系カスケードの活性化を導くエンドトキシンは、遺伝子治療に大きな影響を与えます。
特徴 | EndoFree Plasmid Giga Kit | EndoFree Plasmid Mega Kit | EndoFree Plasmid Maxi Kit |
| Applications | Research on gene therapy, transfection of sensitive cells | Research on gene therapy, transfection of sensitive cells | Research on gene therapy, transfection of sensitive cells |
| Culture volume/starting material | 2.5 liters culture volume | 500 ml – 2.5 liters culture volume | 100–250 ml culture volume |
| Plasmid type | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA |
| Processing | Manual (vacuum) | Manual (vacuum and centrifugation) | Manual (vacuum) |
| Sample per run | 1 sample per run | 1 sample per run | 1 sample per run |
| Time per run | 310 min | 220 min | 150 min |
| Yield | <10 mg | <2.5 mg | <500 µg |
バクテリア細胞はアルカリ性条件下で溶解され、粗ライセートはQIAfilter Cartridgeを用いて清澄化されます。 この段階でEndotoxin Removal Bufferをろ過したライセートに添加し、氷上でインキュベートします。清澄化したライセートを陰イオン交換チップ上にアプライすると、適切な低塩濃度あるいはpH条件でプラスミドDNAが選択的に結合します。RNA、タンパク質、二次代謝物、その他の低分子量不純物が、中濃度の塩による洗浄で取り除かれ、超高純度プラスミドDNAが高塩濃度のバッファーで溶出されます(フローチャート“ QIAGEN Plasmid Kit 操作手順の比較”)。イソプロパノール沈殿によりDNAが濃縮、脱塩され、遠心操作により回収されます。
EndoFree Plasmid Kitsで精製したDNAは以下のような高感度なアプリケーションに最適です。