✓ オンライン注文による24時間年中無休の自動処理システム
✓ 知識豊富で専門的な製品&テクニカルサポート
✓ 迅速で信頼性の高い(再)注文
QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit (50)
カタログ番号 / ID. 52304
✓ オンライン注文による24時間年中無休の自動処理システム
✓ 知識豊富で専門的な製品&テクニカルサポート
✓ 迅速で信頼性の高い(再)注文
特徴
- 高品質で即使用可能なRNAの迅速な精製
- 有機溶媒抽出あるいはアルコール沈殿が不要
- 一定した高い収量
- 夾雑物および酵素阻害物質を完全除去
製品詳細
QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kitは、クエン酸、ヘパリン、EDTAのような一般的な抗凝固剤で処理した新鮮なヒト全血(最高1.5 ml)からシリカメンブレンをベースにした精製法で細胞RNAを分離します。QIAshredder Spin Columnを用いたホモジナイゼーション後、迅速なスピンカラム法によりRNAを簡単に精製します。精製はQIAcube上で完全自動化が可能です。
パフォーマンス
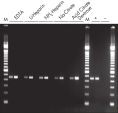
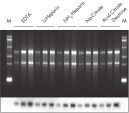
QIAamp調製法は、完全にRNase、夾雑物および酵素阻害物質を除去するので、全てのダウンストリームアプリケーションに最適な高品質RNAが得られます(図 " ノーザンブロット解析用の高品質RNA " および " RT-PCR解析")。
QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit を用いれば、DNA のコンタミを最小限に抑えた最高品質のRNAが調製できます。しかしどのようなRNA 精製法を用いても、わずかなDNA コンタミは避けられません。DNA に非常に高感度なRNAアプリケーションの場合には、残存するDNAの完全な除去が必要となります。このような場合には、QIAamp RNA調製中に簡便なカラム上で、サンプルのDNase 処理が行なえるQIAGEN RNase-Free DNase Set のご使用をお薦めします。
原理
QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit を使用すれば、シリカメンブレンテクノロジーによって細胞RNAを精製することができます。フェノール/クロロホルム抽出は不要です。RNAは選択的にQIAampシリカゲルメンブレンに結合し、夾雑物は洗い流されます。2価の陽イオンおよびタンパク質などのPCR阻害物質は2回の効率的な洗浄ステップにより完全に除去され、残った高純度のRNAが水あるいはキットに添付のバッファーで溶出されます。
QIAampテクノロジーによって、新鮮血液などのサンプルから細胞性トータルRNAを精製し、RT-PCRおよびブロッティング操作ですぐに使用することができます。QIAampによるサンプル調製テクノロジーは、ライセンス保証されています。
操作手順
アプリケーション
QIAamp RNA Blood Mini Kit は、1.5 ml までのクエン酸塩、ヘパリン、EDTA 等の一般的抗凝血剤入りの新鮮なヒト全血から細胞性RNA を精製するキットです。組織サンプルからは、トータルRNA を本キットで精製することが可能です。
裏付けデータと数値
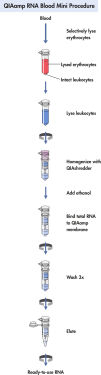
QIAamp RNA Blood Mini procedure.
仕様
| 特徴 | 仕様 |
|---|---|
| ApplicationsJA | PCR, real-time PCR, microarray |
| Elution volume | 30–100 µl |
| Main sample type | Whole blood, tissue |
| Purification of total RNA, miRNA, poly A+ mRNA, DNA or protein | Cellular RNA |
| Sample amount | 50–1.5 ml |
| Format | Spin columns |
| Processing | Manual (centrifugation) |
| Time per run or per prep | <1 hour |
| Technology | Silica technology |
| Yield | 1–5 µg |