✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
RNeasy Lipid Tissue Mini Kit (50)
Cat no. / ID. 74804
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- Optimized lysis conditions for fatty tissues and other tissues
- High yields of total RNA without phenol contamination
- High-quality RNA for all downstream applications
Product Details
The RNeasy Lipid Tissue Mini Kit includes QIAzol Lysis Reagent for lysing fatty tissues and other types of tissue, and RNeasy spin columns for purifying up to 100 µg of high-quality RNA. The kit can be automated using the QIAcube Connect. Tissue samples can be conveniently stabilized using RNAprotect Tissue Reagent (nonfatty tissues only) or Allprotect Tissue Reagent, and efficiently disrupted using a TissueRuptor or TissueLyser system.
Performance
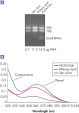
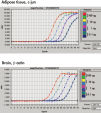
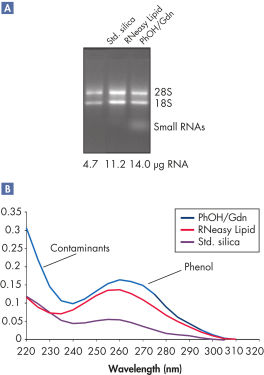
The RNeasy Lipid Tissue protocol integrates QIAzol lysis with RNeasy RNA isolation for high yields of total RNA from fatty tissues with an average yield of RNA from 10 mg of brain of 10 µg, and 2.4 µg of RNA from a 10 mg sample of adipose tissue. RNeasy Lipid Tissue Kit provide efficient isolation of high-quality total RNA without phenol carryover (see figure " High yields of RNA without phenol carryover"). The RNA from fatty tissues is suitable for downstream applications including real-time RT-PCR (see figure " Real-time analysis of high-quality RNA").
Principle
RNeasy Lipid Tissue Kit is optimized for use with fatty tissues, such as brain and adipose tissue. The convenient RNeasy Lipid Tissue protocol integrates optimized phenol/guanidine-based lysis with proven RNeasy purification for isolation of high yields of high-quality total RNA. The combination of organic extraction and chaotropic disruption contributes to the high lysis efficiency of QIAzol Lysis Reagent. Since the RNeasy procedures enrich for mRNA and other RNA species >200 nucleotides, the total RNA yield does not include 5S rRNA, tRNA, and other low-molecular-weight RNAs, which make up 15-20% of total cellular RNA.
Procedure
Applications
RNeasy Lipid Tissue Kit provides easy and efficient isolation of high-quality RNA for all downstream applications, including NGS and real-time RT-PCR.
Supporting data and figures
High yields of RNA without phenol carryover.
Specifications
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Sample amount | 10–100 mg |
| Yield | 2.4–10 mg |
| Technology | Silica technology |
| Processing | Manual |
| Purification of total RNA, miRNA, poly A+ mRNA, DNA or protein | RNA |
| Elution volume | 30–100 µl |
| Main sample type | Fatty tissue samples |
| Time per run or per prep | 45 minutes |
| Format | Spin column |