Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads
미량의 His 태그 단백질에 대한 고처리량 정제 및 His 태그를 사용한 다목적 자기 포획 분석에 사용
미량의 His 태그 단백질에 대한 고처리량 정제 및 His 태그를 사용한 다목적 자기 포획 분석에 사용
Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads는 Ni-NTA Agarose 친화성 정제 기질로 코팅된 자성 입자입니다. His 태그가 있는 재조합 단백질을 고정화하고 정제하는 데 사용됩니다. His 태그의 히스티딘 잔류물은 고정화 니켈 이온의 배위 영역의 빈 위치에 높은 특이성과 친화성으로 결합됩니다. 단백질이 결합되면 자석을 사용하여 비드를 침전시키고 세척한 후 기본 또는 변성 조건에서 소량의 완충액에 단백질을 용출할 수 있습니다.
Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads(그림 Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads 현미경 사진 참조)를 포함하여 QIAexpress Ni-NTA Protein Purification System은 6개 이상의 히스티딘 잔류물의 친화성 태그(His 태그)를 포함하는 단백질에 대한 특허받은 Ni-NTA(nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid) 수지의 뛰어난 선택성을 기반으로 합니다. 이 기술을 사용하면 기본 또는 변성 조건의 모든 발현 시스템에서 거의 모든 His 태그 단백질을 한 번에 정제할 수 있습니다(그림 Ni-NTA 단백질 정제 시스템을 사용한 단백질 정제 참조). 니켈 이온에 대한 킬레이트화 부위가 4개인 NTA는 금속 이온과 상호 작용할 수 있는 부위가 3개뿐인 금속 킬레이트 정제 시스템보다 니켈을 더 단단히 결합합니다. 여분의 킬레이트화 부위는 니켈 이온 침출을 방지하여 다른 금속 킬레이트화 정제 시스템을 사용하여 얻은 것보다 결합력과 순도가 더 높은 단백질 제제를 생성합니다. QIAexpress 시스템은 baculovirus, 포유류 세포, 효모, 박테리아를 포함한 모든 발현 시스템에서 His 태그 단백질을 정제하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
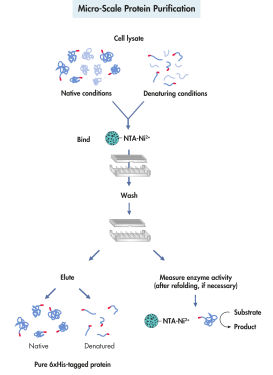
His 태그 단백질의 정제는 세포 용해, 결합, 세척, 용출의 4단계로 구성됩니다(그림 미량의 단백질 정제 참조). QIAexpress 시스템을 사용한 재조합 단백질의 정제는 단백질 또는 His 태그의 3차원 구조에 의존하지 않습니다. 따라서 기본 또는 변성 조건에서 희석액과 미가공 용해물에 있는 단백질을 한 번에 정제할 수 있습니다. 강력한 변성제와 세제는 수용체와 막 단백질 그리고 봉입체를 형성하는 단백질을 효율적으로 용해화하고 정제하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다. 비특이적으로 결합하는 오염 물질을 효율적으로 제거할 수 있는 시약을 세척 완충액에 포함할 수 있습니다(표 참조). 정제된 단백질은 100~250mM 이미다졸을 경쟁 요소로 추가하거나 pH를 낮춰 온화한 조건에서 용출합니다.
| 변성제 | 세제 | 환원제 | 기타 | 염 | 장기 보관용 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 M Gu·HCl | 2% Triton X-100 | 20mM β-ME | 50% 글리세롤 | 4M MgCl2 | 최대 30% 에탄올 |
| 8M urea | 2% Tween 20 | 10mM DTT | 20% 에탄올 | 5mM CaCl2 | 또는 100mM NaOH |
| 1% CHAPS | 20mM TCEP | 20mM 이미다졸 | 2M NaCl |
Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads를 비롯한 QIAexpress Ni-NTA Protein Purification System은 단백질을 신뢰할 수 있는 단일 단계로 정제하여 다음을 포함한 모든 응용 분야에 적합합니다.
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Applications | 단백질체학 |
| Processing | 자동/수동 |
| Yield | 컬럼당 단백질 10mg 미만 |
| Bead size | 20~70µm |
| Support/matrix | 자기 아가로오스 비드 |
| Tag | 6xHis tag |
| Special feature | 높은 처리량(96-well) |
| Start material | 세포 용해물 |
| Binding capacity | 현탁액 최대 2mg/ml(5%) |
| Scale | 미량 |