지방이 많은 조직에서 total RNA 100 ug까지 분리 정제할 수 있습니다
✓ 연중무휴 하루 24시간 자동 온라인 주문 처리
✓ 풍부한 지식과 전문성을 갖춘 제품 및 기술 지원
✓ 신속하고 안정적인 (재)주문
RNeasy Lipid Tissue Mini Kit (50)
카탈로그 번호 / ID. 74804
✓ 연중무휴 하루 24시간 자동 온라인 주문 처리
✓ 풍부한 지식과 전문성을 갖춘 제품 및 기술 지원
✓ 신속하고 안정적인 (재)주문
특징
- 지방조직에 적합한 최적화된 lysis 조건
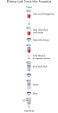
- QIAzol lysis와 RNeasy purification의 통합 — 따라하기 쉬운 protocol
- Phenol contamination 없이 고효율의 total RNA 분리
제품 세부 정보
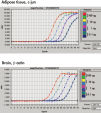
성능
원리
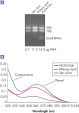
RNeasy Lipid Tissue Kits are optimized for use with fatty tissues, such as brain and adipose tissue. The convenient RNeasy Lipid Tissue protocol integrates optimized phenol/guanidine-based lysis with proven RNeasy purification for isolation of high yields of high-quality total RNA. The combination of organic extraction and chaotropic disruption contributes to the high lysis efficiency of QIAzol Lysis Reagent. Since the RNeasy procedures enrich for mRNA and other RNA species >200 nucleotides, the total RNA yield does not include 5S rRNA, tRNA, and other low-molecular-weight RNAs, which make up 15-20% of total cellular RNA.
절차
응용 분야
RNeasy Lipid Tissue Kits provide easy and efficient isolation of high-quality RNA for all downstream applications, including array analysis and real-time RT-PCR.
지원되는 데이터 및 수치
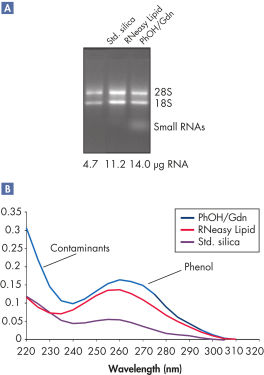
High yields of RNA without phenol carryover.
사양
| 특징 | 사양 |
|---|---|
| Sample amount | 10–100 mg |
| Yield | 2.4–10 mg |
| Technology | Silica technology |
| Processing | Manual |
| Purification of total RNA, miRNA, poly A+ mRNA, DNA or protein | RNA |
| Elution volume | 30–100 µl |
| Main sample type | Fatty tissue samples |
| Time per run or per prep | 45 minutes |
| Format | Spin column |