ipsogen CALR RGQ PCR Kit CE
For broad, sensitive and reliable CALR mutation detection to improve patient diagnosis
For broad, sensitive and reliable CALR mutation detection to improve patient diagnosis

Cat. No. / ID: 674023
The ipsogen CALR RGQ PCR Kit is a ready-to-use CE-IVD kit intended for the detection of CALR mutations in genomic DNA from subjects suspected of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN). The ipsogen CALR RGQ PCR Kit also enables the identification of the two major CALR mutations (Type 1 and Type 2), and is to be used with the QIAGEN Rotor-Gene Q MDx 5Plex HRM Platform. The kit is intended for use by professionals, such as technicians and physicians, who are trained in molecular biology techniques.
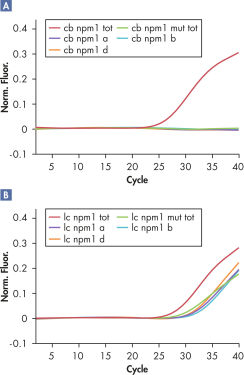
To ensure sensitivity and accuracy, the ipsogen CALR RGQ PCR Kit has been optimized to perform seven separate PCR amplification reactions in a single run for the identification of the two major CALR mutations (Type 1 and Type 2) and the detection of additional minor variants in genomic DNA extracted from human peripheral whole blood. As shown in the figure entitled ' Results generated by the ipsogen CALR RGQ PCR Kit ', the kit identifies CALR mutations Type 1 and Type 2, and detects additional mutations in the CALR exon 9 region (c.1091_1162).
The limit of detection (LoD) of the kit was determined to be 0.60% for the Type 1 CALR mutation and 0.08% for the Type 2 CALR mutation, respectively. The clinical performance was validated using 227 patient samples and showed sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 97.7% at an overall concordance of 98.7% compared to sequencing-based reference methods. >
The ipsogen CALR RGQ PCR Kit is a real-time PCR test for the qualitative detection of somatic mutations in the region c.1091_1162 (cDNA annotation) of exon 9 in the CALR gene (GenBank Accession Number CR457070) (3, 4), and also enables the identification of the two major CALR mutations (Type 1 and Type 2). The kit provides reagents to perform seven separate PCR amplification reactions in the same run for the identification of CALR mutations Type 1 and Type 2, and the detection of additional minor variants in genomic DNA (gDNA) extracted from human peripheral whole blood. The turnaround time to execute all tasks, from gDNA extraction (using manual or automated extraction) to data analysis, is less than one working day.
To validate and control the PCR reaction in the presence of human gDNA template, each CALR reaction mix includes primers and probe to amplify an endogenous sequence of the ABL1 housekeeping gene. This control sequence is amplified through a multiplex PCR reaction in all CALR mutant and wild-type DNA. All required components are included in the run to provide accurate and sensitive detection of CALR mutations.
Results analysis and interpretation is automated and simplified with the Rotor-Gene AssayManager v2.1 software.
The ipsogen CALR RGQ PCR Kit allows detection of CALR mutations and specific identification of Types 1 and 2 on Rotor-Gene Q MDx 5plex HRM. Genomic DNA is first extracted from human peripheral whole blood using the QIAamp DSP Blood Mini Kit (manual) or QIAsymphony SP-automated solution, followed by determination of quality and quantity, and gDNA amplification by real-time PCR. Results interpretation is automated using the Rotor Gene AssayManager v2.1 software. The kit provides all required reagents to perform 7 separate qPCR amplification reactions in the same run for detection of CALR mutations and identification of Types 1 and 2 in genomic DNA extracted from human peripheral whole blood. Simply start the reaction on the Rotor-Gene Q MDx 5plex HRM using the optimized protocols as described in the kit handbook.
The ipsogen CALR RGQ PCR Kit for in vitro diagnostic use enables sensitive and reliable detection of CALR exon 9 mutations, as well as identification of the two major CALR mutations (Type 1 and Type 2). Detection of CALR mutations is now part of the reference World Health Organization (WHO) 2016 criteria for the diagnosis of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN) (2), and presence of this mutation is a major criterion for diagnostic confirmation. The prognostic significance of CALR mutations have also been described (5).