Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads
用于高通量、微型 His 标记蛋白纯化,以及使用 His 标记进行多功能磁性捕获检测
用于高通量、微型 His 标记蛋白纯化,以及使用 His 标记进行多功能磁性捕获检测
Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads 是涂有 Ni-NTA Agarose 亲和纯化基质的磁微粒。它们用于固定和纯化带有 His 标记的重组蛋白。His 标签中的组氨酸残基凭借高特异性和亲和力,与固定镍离子配位球中的空位结合。蛋白结合后,可使用磁铁将微珠沉淀、洗涤,然后在原生或变性条件下用少量缓冲液洗脱蛋白。
QIAexpress Ni-NTA 蛋白纯化系统,包括 Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads(见图 Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads 的显微图),基于的是获得专利的 Ni-NTA(次氮基三乙酸镍)树脂对含有六个或更多组氨酸残基亲和标记(His 标记)的蛋白的显著选择性。该技术可在原生或变性条件下,从任何表达系统中一步纯化几乎所有 His 标记蛋白(见图 使用 Ni-NTA 蛋白纯化系统进行蛋白纯化)。NTA 有四个镍离子螯合位点,与只有三个位点可与金属离子相互作用的金属螯合纯化系统相比,NTA 与镍的结合更紧密。额外的螯合位点可防止镍离子浸出,与其他金属螯合纯化系统相比,它的结合能力更强,制备的蛋白纯度更高。QIAexpress 系统可用于从任何表达系统中纯化 His 标签蛋白,包括杆状病毒、哺乳动物细胞、酵母和细菌。
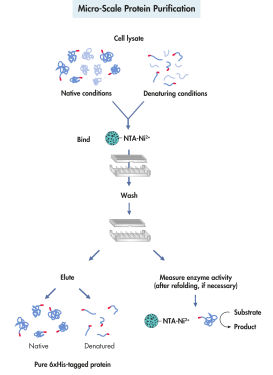
His 标记蛋白的纯化分为 4 个阶段:细胞裂解、结合、洗涤和洗脱(见图 微型蛋白纯化)。使用 QIAexpress 系统纯化重组蛋白与蛋白或 His 标记的三维结构无关。这样就可以在非变性或变性条件下,从稀释溶液和粗裂解物中一步纯化蛋白。强变性剂和洗涤剂可用于高效溶解和纯化受体、膜蛋白和形成包涵体的蛋白。洗涤缓冲液中可加入能高效去除非特异性结合污染物的试剂(见表)。通过添加 100–250 mM 咪唑作为竞争剂或降低 pH 值,在温和条件下洗脱纯化的蛋白。
| 变性剂 | 洗涤剂 | 还原剂 | 其他 | 盐 | 用于长期储存 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 M Gu·HCl | 2% Triton X-100 | 20 mM β-ME | 50% 甘油 | 4 M MgCl2 | 高达 30% 的乙醇 |
| 8 M 尿素 | 2% 吐温 20 | 10 mM DTT | 20% 乙醇 | 5 mM CaCl2 | 或 100 mM NaOH |
| 1% CHAPS | 20 mM TCEP | 20 mM 咪唑 | 2 M NaCl |
QIAexpress Ni-NTA 蛋白纯化系统(包括 Ni-NTA Magnetic Agarose Beads)可为以下任何应用提供可靠的一步蛋白纯化:
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Applications | 蛋白质组学 |
| Processing | 自动/手动 |
| Yield | 每柱 <10 mg 蛋白 |
| Bead size | 20–70 µm |
| Support/matrix | 磁性琼脂糖珠 |
| Tag | 6xHis 标签 |
| Special feature | 高通量(96 孔) |
| Start material | 细胞裂解物 |
| Binding capacity | 最多 2 mg/ml 悬浮液 (5%) |
| Scale | 微型 |