Rotor-Gene SYBR® Green PCR Demo Kit
用于评估Rotor-Gene Q实时荧光定量PCR分析仪的性能
用于评估Rotor-Gene Q实时荧光定量PCR分析仪的性能
✓ 全天候自动处理在线订单
✓ 博学专业的产品和技术支持
✓ 快速可靠的(再)订购
Cat. No. / ID: 204001
✓ 全天候自动处理在线订单
✓ 博学专业的产品和技术支持
✓ 快速可靠的(再)订购
Rotor-Gene SYBR Green PCR Demo Kit配合Rotor-Gene预混液,用于展现Rotor-Gene Q实时荧光定量PCR分析仪的性能。试剂盒包含所有需要的反应组分,来通过SYBR Green-based real-time PCR对基因组DNA靶标进行定量。这包括预稀释的基因组DNA标准物、2个未知样本、优化的预混液和人G蛋白耦联雌激素受体1(GPER)基因的特异性引物对。使用此试剂盒可评估Rotor-Gene Q实时荧光定量PCR分析仪进行基因定量时的可靠性、可重复性和灵敏度。
Rotor-Gene Kits配合Rotor-Gene Q实时荧光定量PCR分析仪可完成高精度real-time PCR。Rotor-Gene Kits中提供的即用型预混液可快速、准确的进行基因定量,无需反应优化,而Rotor-Gene Q实时荧光定量PCR分析仪采用独特的离心转子设计。PCR管放置到转子中,离心的PCR管穿过一道激发光源和一个流动空气腔内的检测器。这意味着管间几乎没有光照和温度变化,使real-time PCR定量分析具有高精度。此外,由于转子离心速度持续在400 rpm,使高速数据采集成为可能。
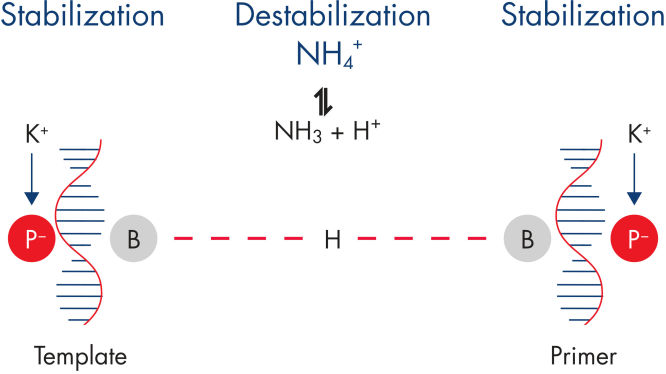
使用Rotor-Gene SYBR Green PCR Demo Kit可确保高度特异性的扩增,离子的平衡组合可减少非特异性引物退火(参见" Specific primer annealing")。使用Q-Bond可进行快速循环,不影响性能,Q-Bond是一种新颖的PCR添加剂,使PCR运行时间可少至45分钟(参见" Fast primer annealing")。
使用Rotor-Gene SYBR Green PCR Demo Kit进行SYBR Green法real-time PCR,可定量不同的基因组DNA靶标的拷贝数。每个反应包含:
Rotor-Gene SYBR Green PCR Demo Kit手册包含3个实验方案。Rotor-Gene用户可选用手工反应体系构建的实验方案或使用QIAgility自动化反应体系构建的实验方案。反应体系构建后,用户可选择在Rotor-Gene Q实时荧光定量PCR分析仪上进行real-time PCR的实验方案。
使用QIAgility可避免手工移液步骤,紧凑的台式仪器可进行快速、高精度的PCR反应体系构建,可减少或消除由于人为失误造成的反应体系构建错误。QIAgility可配合Rotor-Gene Q实时荧光定量PCR分析仪和Rotor-Gene Kits使用,可简单分装液体到单管、联管和Rotor-Discs。
通过一套标准物(2000、1000、500、250和125个拷贝;每个标准物有4个平行分析)的CT值可产生一条标准曲线。标准曲线用来确定2个未知样本(500和250个拷贝;每个未知样本有24个重复[当手工反应体系构建时,每个未知样本可最少有4个重复])的拷贝数。此外,还进行4个无模板对照(NTC)反应。因此,在Rotor-Gene Q实时荧光定量PCR分析仪上有72个反应同时进行。
Rotor-Gene SYBR Green PCR Demo Kit用于评估Rotor-Gene Kits配合Rotor-Gene Q实时荧光定量PCR分析仪的性能。此试剂盒与Rotor-Gene 3000或Rotor-Gene 6000兼容。使用此试剂盒可评估Rotor-Gene Q实时荧光定量PCR分析仪在基因定量时的精确度和可重复性。