✓ 全天候自动处理在线订单
✓ 博学专业的产品和技术支持
✓ 快速可靠的(再)订购
特点
- 创新的数学方法进行HRM分析
- supervised模式进行高度精确的基因型鉴定
- unsupervised模式自动检测新突变
- 统计学方法分类并分析HRM数据
- 最少的人工,流程标准化的数据分析
产品详情
Rotor-Gene ScreenClust HRM Software是一款功能强大的高分辨率熔解(HRM)数据分析工具,可分析Rotor-Gene Q实时荧光定量PCR分析仪或Rotor-Gene 6000分析仪的数据。Rotor-Gene ScreenClust HRM Software通过将样品进行分组,用于诸如基因分型和突变扫描等应用。
绩效
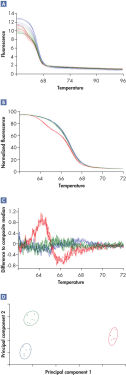
Rotor-Gene Q实时荧光定量PCR分析仪与Rotor-Gene ScreenClust HRM Software联用甚至可鉴定高难度的class IV A/T SNP,这些序列熔解温度的差异可能小至0.1°C(参见"I dentification of a class IV SNP")。
在基因突变检测实验中,对EGFR基因外显子19中由基因插入或缺失引起的突变进行分析(参见" Successful mutation detection")。Rotor-Gene ScreenClust HRM Software 将数据分为前3个主要成分,精确地分离了多个相近且部分覆盖的熔解概况,对6个假定未知及野生型样品均进行了正确的区分。
原理
HRM是一种创新的技术,基于双链PCR产物随着温度的升高从双链裂解为单链的熔解过程的行为差异,对其进行鉴定。首先通过PCR 扩增靶序列。然后通过高度精确的PCR产物熔解,根据序列、长度、GC含量或链互补性对样本进行区分,可检测到单碱基对的变化。事先无需知道序列信息,即可以直接简单的方式检测未知的甚至是复杂的序列变化。
可靠的HRM分析需要合适的HRM仪器、化学试剂和数据分析软件。Rotor-Gene Q实时荧光定量PCR分析仪独特的转子设计使其具备卓越的热学和光学表现,是HRM分析的理想仪器。Type-it HRM PCR Kit提供经优化的化学试剂,进行精确的序列变化分辨以及明确的等位基因检测。
HRM数据分析通过对比不同样品熔解曲线的位置和形状鉴定基因型。杂合子和纯合子的熔解曲线的形状和熔解点(Tm)是不同的。在标准的HRM软件包中,对比待测样品与对照样品的熔解曲线的形状和位置以区分不同样品。这个方法有可能会获得不可靠的、难以分析的结果,同时可能需要耗时的人工分析。相反地,Rotor-Gene ScreenClust HRM Software应用创新的数学运算法则鉴定样品,并对其进行分类。
程序
Rotor-Gene ScreenClust HRM Software通过下列4步分析数据:
- 标准化
- 生成残差图
- 主要成分分析
- 聚类
该软件为用户提供全程指导,给出每一步可做的相关选择的信息。
在Rotor-Gene热循环仪上进行的HRM实验生成的原始数据(*.rex 文档)可使用Rotor-Gene ScreenClust HRM Software进一步分析。在分析的第一步,将曲线缩放到最适合的一条线上,使最高荧光值相当于100,最低的相当于0,从而实现数据标准化。然后分化曲线,通过所有样品的中间荧光值获得一条成分中线。从这个成分中线中减去每个样品的熔解轨迹,绘出残差图。分析残差图,抽提出主要成分,对单个样品进行鉴定。主要成分分析是一种广泛使用的数据分析方法,而Rotor-Gene ScreenClust HRM Software是第一款对HRM数据进行主要成分分析的应用软件。主要成分分析强调数据中的相似点和不同点,以supervised或unsupervised模式生成聚类图。
Rotor-Gene ScreenClust HRM Software根据等位基因对数据进行聚类(分组)。supervised模式通常用于基因类型已知的SNP基因分型,在该模式中,用户对每个聚类设定一个或多个对照样品,软件根据样品的特性对其进行聚类(自动调用)。unsupervised模式用于发现数据中的新突变,此时样品的基因类型是未知的或者是部分已知。在unsupervised模式中,该软件计算聚类的最佳数目。此功能是发现新多态性的理想工具。
两种模式的分析都显示为一个易于理解的聚类图,结果还提供统计学概率和典型性数据,以方便地对比不同实验的结果。所有数据和图片可方便地以各种格式导出,如JPG、PDF、CSV或XLS文档,并且可总结到一个实验报告中。
应用
应用Rotor-Gene ScreenClust HRM Software进行HRM分析,为多种应用提供了巨大的潜力。SNP基因分型、突变扫描或检测实验可最大程度地受益于这项功能强大的技术。
辅助数据和图表
Identification of a class IV SNP.