QIAseq Targeted Methyl Panel (8)
Cat no. / ID. 335501
Features
- Complete system to go from bisulfite-converted DNA to a sequencing-ready library using a single-day workflow
- Error correction with Unique Molecular Indices (UMIs) to enhance NGS panel sensitivity
- The QIAseq enrichment technology approach that increases sensitivity and overcomes targeting challenges compared to other NGS technologies
- Integrated Sample to Insight analysis solutions with cloud-based QIAGEN GeneGlobe or locally-installed QIAGEN CLC Genomics Workbench software
Product Details
QIAseq Targeted Methyl Panels offer a single-day solution capable of targeting thousands of CpG sites in the genome. As with targeted DNA panels, QIAseq solutions are based on the QIAseq enrichment technology that provides a sensitive and specific solution for detecting regions all across the genome.
For customized products, please see our QIAseq Targeted Methyl Custom Panels.
Performance
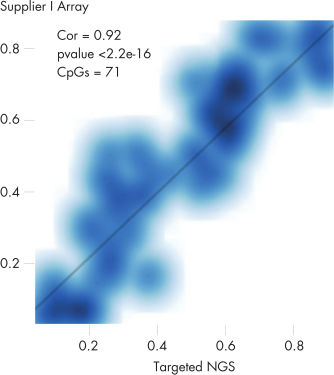
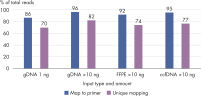
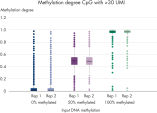
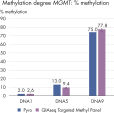
QIAseq Targeted Methyl Panels deliver high mapping efficiency (figure QIAseq Targeted Methyl Panel: mapping efficiency), high reproducibility (figure QIAseq Targeted Methyl Panel: methylation degree reproducibility) and high correlation with established methods (figures QIAseq Targeted Methyl Panel – high correlation with established methods and QIAseq Targeted Methyl Panel: methylation status of FFPE DNA: methylation degree).
Principle
Epigenetics describes the study of heritable changes in gene function that occur without a change in the nuclear DNA sequence. In addition to RNA-associated silencing and histone modification, a major epigenetic mechanism in higher-order eukaryotes is DNA methylation. Epigenetic changes play a crucial role in the regulation of important cellular processes, such as gene expression and cellular differentiation, and were also identified as key factors in various diseases.
DNA methylation occurs on cytosine residues, especially in CpG islands, which are GC-rich regions. They are usually clustered around the regulatory region of genes and can affect their transcriptional regulation. Methylation of CpG islands is known to inactivate gene expression and plays an important role in normal and disease development. Cytosine methylation may also occur in non-CpG content, as described for embryonic stem cells.
QIAseq Targeted Methyl Panels enable Sample to Insight, targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) to interrogate DNA methylation degree. This highly optimized solution facilitates sensitive DNA methylation detection using integrated Unique Molecular Indices (UMIs) from cells, tissues and biofluids. The required amount of template for a single QIAseq Targeted Methyl sequencing reaction ranges from 1–100 ng for fresh gDNA, 10–200 ng for FFPE DNA or 10–100 ng for ccfDNA.
Procedure
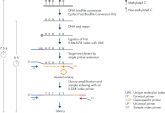
QIAseq Targeted Methyl Panels employ a streamlined workflow (figure QIAseq Targeted Methyl Panel sequencing workflow) for generating focused libraries from multiple input types, including difficult samples such as FFPE and liquid biopsy (ccfDNA). First, bisulfite conversion of isolated DNA is performed (recommended product: EpiTect Fast Bisulfite Kit), followed by DNA end repair. Afterwards, during target enrichment, a Unique Molecular Index (UMI) is added to the DNA library. UMIs are unique barcode sequences that enable bioinformatics analysis to exclude duplicates and error-correct the sample’s methylation status. QIAseq Targeted Methyl Panels utilize the QIAseq enrichment technology, a PCR method that uses a single target-specific primer, with a universal primer. This approach increases the efficiency of design – making it more sensitive for challenging samples, while maximizing the coverage of the regions of interest.
Applications
- Detection of methylation status from FFPE samples
- Detection of methylation status from liquid biopsy
- Detection of cell- and tissue-specific methylation markers
Supporting data and figures
QIAseq Targeted Methyl Panel – high correlation with established methods