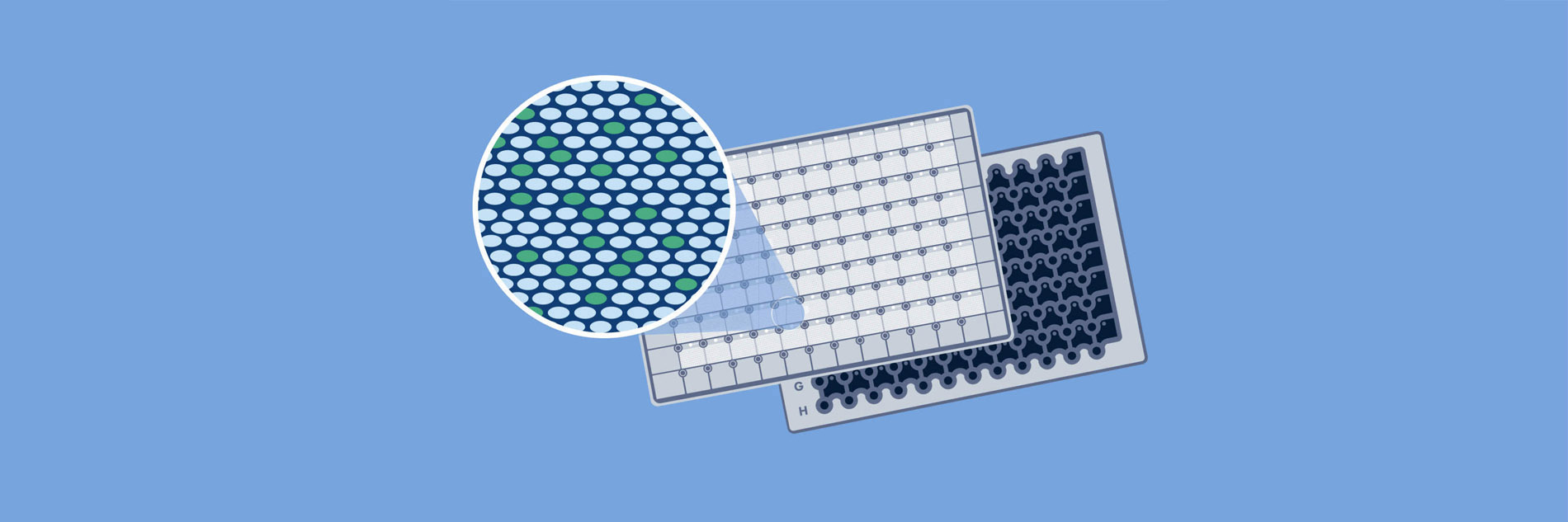
It is easy to use the QIAcuity
Transition into a simple and rapid digital PCR workflow.
Latest in Digital PCR – Webinars, stories and more
Choosing dPCR vs. qPCR
Compare and contrast the two methods to understand which one best suits your needs and learn how to transition your current qPCR assay to dPCR.
Nanoplate dPCR technology
Digital PCR applications
Featured – Delve into digital PCR
Open your inbox to free instant dPCR news
FAQs about QIAcuity Nanoplate Digital PCR
References
Huggett JF et al. (2013). The digital MIQE guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Digital PCR Experiments. Clin Chem. 59(6):892-902.
dMIQE Group, Huggett JF. (2020). The Digital MIQE Guidelines Update: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Digital PCR Experiments for 2020. Clin Chem. 66(8):1012-1029.

